Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
빙수달 게임 개발 노트
[알고리즘] 스택(Stack) 본문
스택(Stack)이란?
스택(stack)은 데이터를 일시적으로 저장하기 위해 사용하는 자료구조로, 데이터의 입력과 출력 순서는 후입선출(LIFO, Last In First Out)이다. 스택에 데이터를 넣는 작업을 푸시(push)라 하고, 스택에서 데이터를 꺼내는 작업을 팝(pop)이라고 한다. 접시를 겹겹이 쌓아 올린 뒤, 가장 마지막에 올린 접시부터 먼저 꺼내게 되는 그림를 떠올리면 이해가 쉽게 될 것이다. 푸시, 팝을 하는 위치를 꼭대기(top)라 하고, 스택의 가장 밑바닥 부분을 바닥(bottom)이라고 한다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stdexcept>
using namespace std;
#define SIZE 1000
class Stack
{
int* arr;
int capacity;
int top_idx;
public:
Stack(int size = SIZE);
~Stack();
void push(int x);
int pop();
int top();
int size();
bool empty();
bool isFull();
};
Stack::Stack(int size)
{
arr = new int[size];
capacity = size;
top_idx = -1;
}
Stack::~Stack()
{
delete[] arr;
}
void Stack::push(int x)
{
if (isFull())
{
throw std::runtime_error("Overflow: Stack is full");
}
cout << "Pushing " << x << endl;
arr[++top_idx] = x;
}
int Stack::pop()
{
if (empty())
{
throw std::runtime_error("Underflow: Stack is empty");
}
return arr[top_idx--];
}
int Stack::top()
{
if (empty())
{
throw std::runtime_error("Underflow: Stack is empty");
}
return arr[top_idx];
}
int Stack::size()
{
return top_idx + 1;
}
bool Stack::empty()
{
return (top_idx == -1);
}
bool Stack::isFull()
{
return (top_idx == capacity - 1);
}
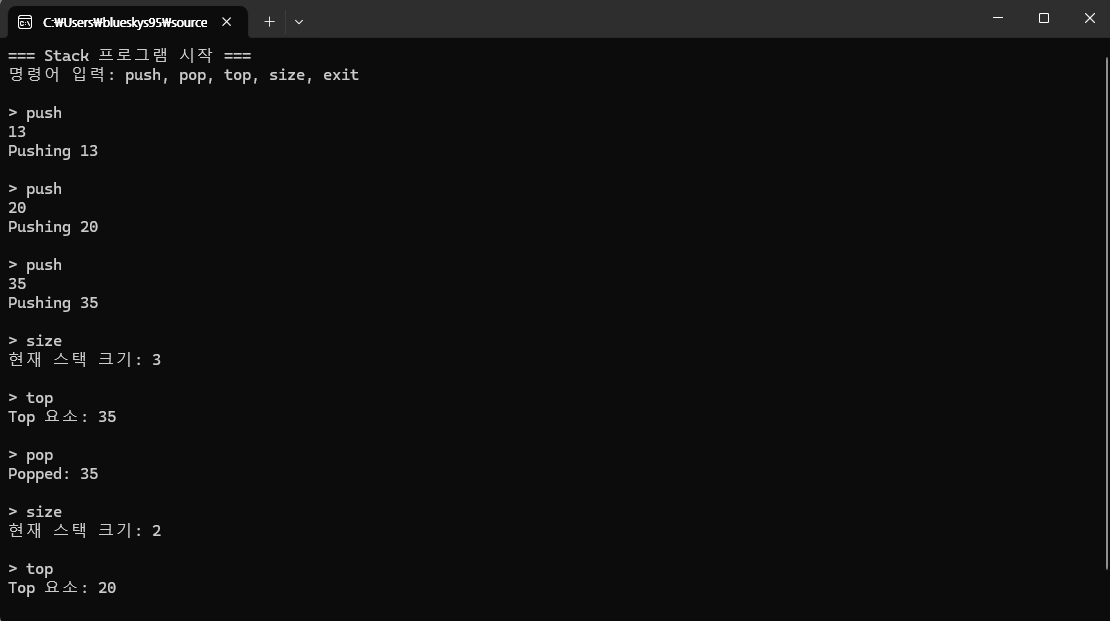
int main()
{
Stack stack(5);
string command;
cout << "=== Stack 프로그램 시작 ===\n";
cout << "명령어 입력: push, pop, top, size, exit\n";
while (true)
{
cout << "\n> ";
cin >> command;
try
{
if (command == "push")
{
int value;
cin >> value;
stack.push(value);
}
else if (command == "pop")
{
int value = stack.pop();
cout << "Popped: " << value << endl;
}
else if (command == "top")
{
cout << "Top 요소: " << stack.top() << endl;
}
else if (command == "size")
{
cout << "현재 스택 크기: " << stack.size() << endl;
}
else if (command == "exit")
{
cout << "프로그램을 종료합니다.\n";
break;
}
else
{
cout << "잘못된 명령어입니다. 다시 입력하세요.\n";
}
}
catch (const std::runtime_error& e)
{
cout << "오류: " << e.what() << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
'Programming > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [알고리즘] 단어 or 정수 역순 정렬 (0) | 2024.12.19 |
|---|---|
| [알고리즘] 모래시계 그리기(* & 숫자) (0) | 2024.12.19 |
| [알고리즘] 정수 A에서 정수 B까지 합 (1) | 2024.12.19 |
| [알고리즘] 세 정수 중 중앙값 구하기 (0) | 2024.12.19 |
| [알고리즘] 최댓값 구하기 (1) | 2024.12.19 |




